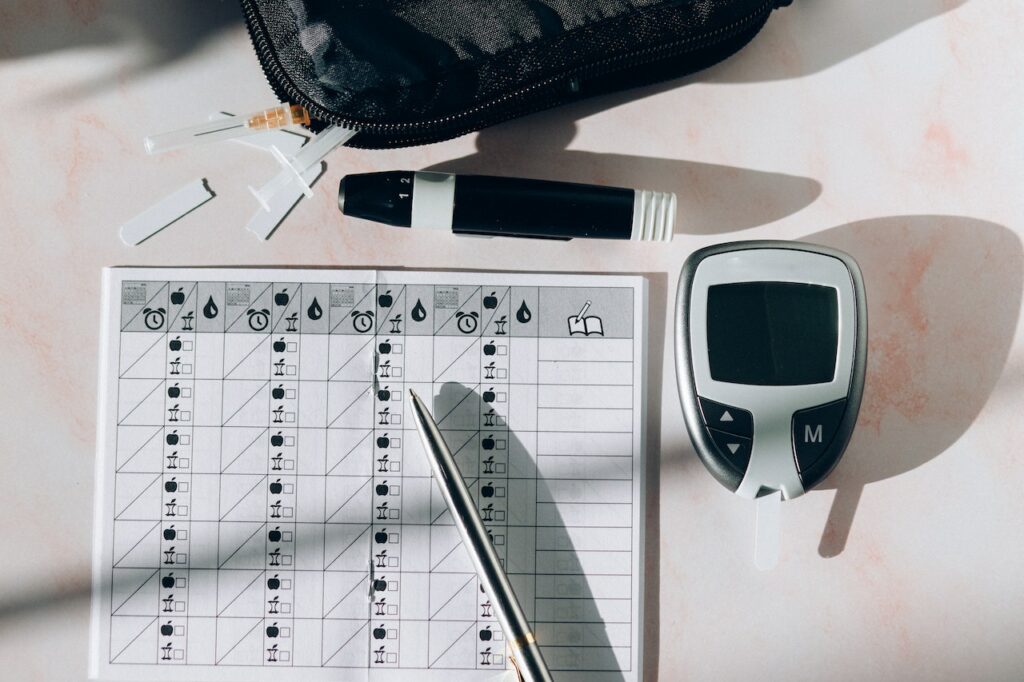
A sugar levels in blood chart helps monitor blood glucose levels for diabetes management. Monitoring blood sugar levels is crucial for diabetes control and prevention of complications.
It provides information about how the body processes glucose and helps determine the effectiveness of medications and lifestyle changes in managing diabetes. By regularly checking blood sugar levels and referring to a sugar levels in blood chart, individuals with diabetes can make informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and insulin or medication dosage.
This chart typically displays target ranges for blood sugar levels before and after meals, as well as fasting glucose levels. Properly managing blood sugar levels is essential for maintaining overall health and preventing diabetes-related complications.
Table of Contents
Importance Of Blood Sugar Control
Maintaining normal blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. Uncontrolled blood sugar levels can have a significant impact on several aspects of our body and can lead to various health complications.
Elevated blood sugar levels, especially over a prolonged period, can result in:
- Increased risk of developing diabetes
- Cardiovascular problems
- Damage to nerves and blood vessels
- Impaired vision or blindness
- Delayed wound healing
- Weak immune system
On the other hand, maintaining normal blood sugar levels offers several benefits, including:
- Reduced risk of developing diabetes
- Improved cardiovascular health
- Reduced risk of nerve and blood vessel damage
- Preserved vision
- Promoted wound healing
- Enhanced immune system function
By maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and medications as prescribed by a healthcare professional, individuals can achieve and sustain normal blood sugar levels, thereby reducing the risk of complications associated with high blood sugar.
Blood Sugar Monitoring Techniques
| Monitoring Technique | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Fingerstick Glucose Test | 1. Quick and simple 2. Relatively inexpensive 3. Can be done at home |
1. Requires finger pricking 2. May cause discomfort 3. Not continuous monitoring |
| Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) | 1. Continuous monitoring 2. Provides real-time data 3. Offers trend analysis |
1. Requires sensor insertion 2. More expensive than fingerstick test 3. Requires calibration |
The fingerstick glucose test is a widely used method for measuring blood sugar levels. It is quick, simple, and can be performed at home. However, it requires finger pricking, which may cause discomfort. Additionally, it does not provide continuous monitoring.
On the other hand, continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) offers continuous monitoring and provides real-time data. It also offers trend analysis, which can be helpful in managing blood sugar levels. However, CGM requires sensor insertion, which may be inconvenient for some. It is also more expensive than the fingerstick test and requires calibration for accurate results.
Interpreting Your Blood Sugar Levels
Learn how to interpret your blood sugar levels using a comprehensive chart. Understand the different ranges and the potential implications for your health.
Normal range of blood sugar levels: The normal range for blood sugar levels varies depending on when the test is taken. Fasting blood sugar levels, taken after at least 8 hours of fasting, should ideally be between 70-99 mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter). Random blood sugar levels, taken at any time of the day, should be below 140 mg/dL. After consuming a meal, blood sugar levels may rise, but should ideally be below 180 mg/dL within 2 hours. Maintaining blood sugar levels within these ranges is important for overall health. Variations in blood sugar levels throughout the day: Blood sugar levels naturally fluctuate throughout the day. They tend to be lowest in the morning after fasting overnight, and gradually rise after meals. Physical activity, stress, and illness can also impact blood sugar levels. Monitoring and maintaining stable blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes to avoid complications. Factors that affect blood sugar levels: Several factors can influence blood sugar levels. Diet plays a significant role, as consumption of carbohydrates and sugary foods can cause spikes in blood sugar levels. Insufficient insulin production or insulin resistance can also result in elevated blood sugar levels. Medications, such as steroids, can affect blood sugar levels as well. It is important to monitor and manage these factors to keep blood sugar levels within a healthy range. Please note that these are general guidelines, and individual blood sugar targets may vary depending on factors such as age, overall health, and any underlying medical conditions. It is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance.:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/the-best-time-to-check-blood-glucose-after-a-meal-701296a8e08949f4890652e8e0689061.jpg)
Credit: www.eatingwell.com
Common Blood Sugar Disorders
Blood sugar disorders are a common health concern affecting many individuals worldwide. These disorders include Type 1 diabetes, Type 2 diabetes, Gestational diabetes, and Pre-diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is characterized by the inability of the body to produce insulin, which leads to high blood sugar levels. On the other hand, Type 2 diabetes is a condition where the body either resists the effects of insulin or doesn’t produce enough insulin to control blood sugar levels adequately. Gestational diabetes occurs in pregnant women and can increase the risk of complications during pregnancy and delivery. Pre-diabetes is a condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not yet classified as diabetes. Monitoring blood sugar levels through a Sugar Levels in Blood Chart can be beneficial for managing and controlling these blood sugar disorders.
Blood Sugar Chart: Decoding The Numbers
Blood sugar levels play a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. Understanding and interpreting a blood sugar chart is essential for individuals with diabetes or those looking to monitor their glucose levels. The target blood sugar levels vary depending on certain factors such as age, gender, and whether the person has been diagnosed with diabetes. For generally healthy individuals, the American Diabetes Association recommends a fasting blood sugar level of 80-130 mg/dL (4.4-7.2 mmol/L) before meals and a level of less than 180 mg/dL (10.0 mmol/L) two hours after a meal. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the specific target levels for each individual. Keeping blood sugar levels within the target range is crucial to prevent complications associated with high blood sugar (hyperglycemia) or low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). Regular monitoring and understanding of blood sugar charts is necessary for successful diabetes management and overall well-being.
Healthy Lifestyle Changes For Glucose Control
One can make healthy lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and managing stress to control glucose levels. Consulting a doctor and using a sugar levels in blood chart can aid in monitoring and maintaining stable sugar levels for overall well-being.
Proper nutrition plays a crucial role in managing blood sugar levels. It is important to focus on eating a balanced diet that includes plenty of fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources. Avoiding sugary and processed foods is essential for maintaining stable glucose levels. Additionally, incorporating regular physical activity into your routine can have a positive impact on blood sugar control. Engaging in exercises such as walking, jogging, or cycling helps to lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. Stress management techniques are also vital for better glucose control. Practicing relaxation techniques like meditation, deep breathing, and yoga can help reduce stress levels and promote stable blood sugar levels. By making these healthy lifestyle changes, individuals can effectively manage their blood sugar levels and promote overall well-being.
Importance of nutrition in blood sugar management
| Nutrition Tips for Blood Sugar Control |
|---|
| Consume a balanced diet with fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein |
| Avoid high-sugar and processed foods |
Physical activity and its impact on blood sugar levels
Regular exercise can help lower blood sugar levels and increase insulin sensitivity. Engaging in activities like brisk walking, jogging, or cycling for at least 30 minutes a day can provide significant benefits for blood sugar control.
Stress management techniques for better glucose control
Managing stress is crucial for maintaining stable blood sugar levels. Practices like meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga can help alleviate stress and promote better glucose control.
Medication And Treatment Options For Blood Sugar Control
Find effective medication and treatment options on the blood sugar control chart to manage sugar levels for better health. Explore various methods to regulate blood sugar naturally and promote overall well-being.
When it comes to blood sugar control, there are various medication and treatment options available. Oral medications are commonly prescribed for diabetes management. These medications work by helping the body use insulin more efficiently or by stimulating the pancreas to produce more insulin. Insulin therapy is another treatment option for blood sugar control, especially for individuals with type 1 diabetes or advanced type 2 diabetes. Insulin is usually injected using a syringe, insulin pen, or an insulin pump. It is crucial to work closely with your healthcare provider to determine the right insulin dosage and monitor your blood sugar levels regularly. Other treatment options for blood sugar control may include lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, a healthy diet, and weight management. In some cases, bariatric surgery may be recommended for individuals with obesity and uncontrolled diabetes. Remember to consult with your healthcare provider to find the best treatment approach for your specific needs.| Medication and Treatment Options for Blood Sugar Control |
| Oral medications for diabetes management |
|
– Help the body use insulin more efficiently – Stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin |
| Insulin therapy and its effectiveness |
|
– Suitable for individuals with type 1 diabetes or advanced type 2 diabetes – Administered through injection (syringe, insulin pen, or insulin pump) – Close monitoring of blood sugar levels is crucial |
| Other treatment options for blood sugar control |
|
– Lifestyle changes (exercise, healthy diet, weight management) – Bariatric surgery for individuals with obesity and uncontrolled diabetes – Consult with healthcare provider for personalized treatment approach |
Preventing And Managing Blood Sugar Fluctuations
Managing blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing it. By preventing spikes and drops in blood sugar, one can maintain stable glucose levels. It is important to recognize the symptoms of hypo- and hyperglycemia, as each requires different actions. Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, can cause dizziness, fatigue, and confusion. Consuming small, frequent meals that contain carbohydrates can help raise blood sugar levels. Hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar, may present symptoms such as frequent urination, increased thirst, and blurred vision. Taking prescribed medications, exercising regularly, and following a healthy diet low in carbohydrates can help prevent high blood sugar levels. Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly and seeking immediate medical attention if significant fluctuations occur is essential for proper management.
Long-term Strategies For Mastering Glucose Control
| Long-term Strategies for Mastering Glucose Control |
| Creating a personalized glucose control plan |
For those looking to master glucose control in the long term, it is important to create a personalized plan tailored to individual needs. This involves setting specific goals that take into account factors such as activity levels, diet, and medication. Regular medical check-ups and monitoring are crucial in ensuring progress towards these goals. Monitoring blood sugar levels at home using a glucometer can provide valuable insights into how different activities and meals affect glucose control. It is also essential to stay informed about support resources available for better management. These resources can include educational materials, self-help groups, and online communities where individuals can share experiences and learn from others. By following a personalized glucose control plan and utilizing available support resources, individuals can take proactive steps towards better managing their blood sugar levels.
Frequently Asked Questions On Sugar Levels In Blood Chart
What Are Normal Blood Sugar Levels?
Normal blood sugar levels range from 80-120 mg/dL after fasting and before meals. After meals, it is considered normal if it stays below 180 mg/dL. Consistently high or low levels may indicate a health issue and should be discussed with a healthcare professional.
What Causes High Blood Sugar Levels?
High blood sugar levels can be caused by factors such as poor diet, lack of physical activity, stress, certain medications, and medical conditions like diabetes. Insulin resistance or insufficient insulin production can also contribute to high blood sugar levels.
How Can I Lower My Blood Sugar Levels?
To lower blood sugar levels, it is important to maintain a healthy diet, exercise regularly, manage stress levels, and take any prescribed medications as directed. Consuming foods low in carbohydrates and sugar, increasing fiber intake, and staying hydrated can help regulate blood sugar levels.
What Are The Symptoms Of Low Blood Sugar?
Symptoms of low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) include dizziness, shakiness, sweating, confusion, headache, irritability, and weakness. If experiencing these symptoms, consuming a small amount of sugar or a glucose tablet can help raise blood sugar levels.
Conclusion
Understanding blood sugar levels is crucial for maintaining good health. By regularly monitoring and interpreting the sugar levels in your blood chart, you can make informed decisions about your diet, lifestyle, and medication. Keep in mind that these numbers can vary for each individual, so it’s important to consult with your healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
Taking proactive steps to manage your blood sugar levels can lead to better overall health and reduce the risk of complications related to diabetes. Stay informed, stay healthy!